Hello everyone,
In my undergraduate studies, I learnt Verilog before VHDL and hence I prefer to design in Verilog. In Verilog, there are just two data types for design, namely wire and reg. However, in VHDL, a signal / variable can be of different types like integer, std_logic, unsigned, signed etc. All these data types are used in different situation, eg: '+' operator is commonly used with unsigned data type.
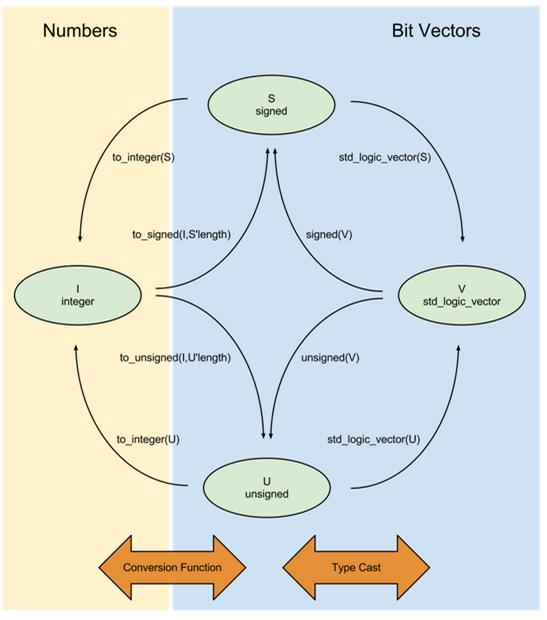
For Verilog users who are migrating to VHDL, this becomes confusing to remember all the conversion functions. I found a figure which clearly shows all the conversion functions.
In my undergraduate studies, I learnt Verilog before VHDL and hence I prefer to design in Verilog. In Verilog, there are just two data types for design, namely wire and reg. However, in VHDL, a signal / variable can be of different types like integer, std_logic, unsigned, signed etc. All these data types are used in different situation, eg: '+' operator is commonly used with unsigned data type.
For Verilog users who are migrating to VHDL, this becomes confusing to remember all the conversion functions. I found a figure which clearly shows all the conversion functions.
Answer record from Xilinx provides an example design of some conversion functions.